Have you ever looked up at the sky and marveled at the grace and beauty of birds? These feathered creatures have fascinated humans for centuries.
But have you ever wondered what truly makes a bird a bird? Understanding the main characteristics of birds can deepen your appreciation for these incredible animals. You’ll discover the unique traits that define our avian friends. From their lightweight bones to their specialized beaks, each feature serves a purpose.
As you read on, you’ll unlock the secrets that have allowed birds to soar, sing, and thrive in every corner of the world. Get ready to explore the wonders of avian life and see the world through a bird’s eye view.
Physical Features
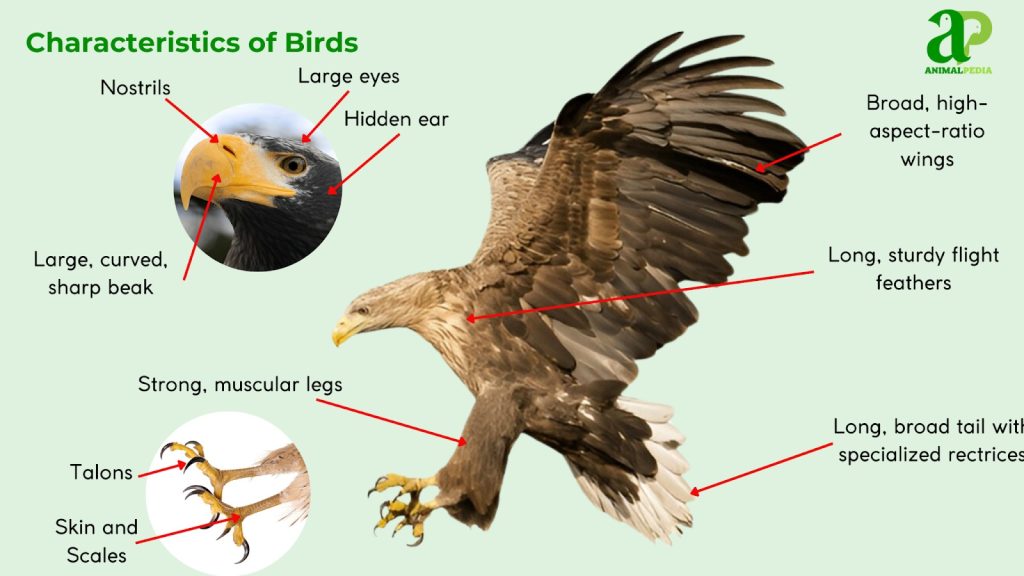
Birds have unique physical features that help them live and move. These features make birds different from other animals.
Understanding these features helps us learn how birds survive in their environments.
Feathers And Plumage
Feathers cover a bird’s body. They keep birds warm and dry. Feathers also help birds fly and attract mates.
Plumage means the pattern and color of feathers. Different birds have different colors for camouflage or display.
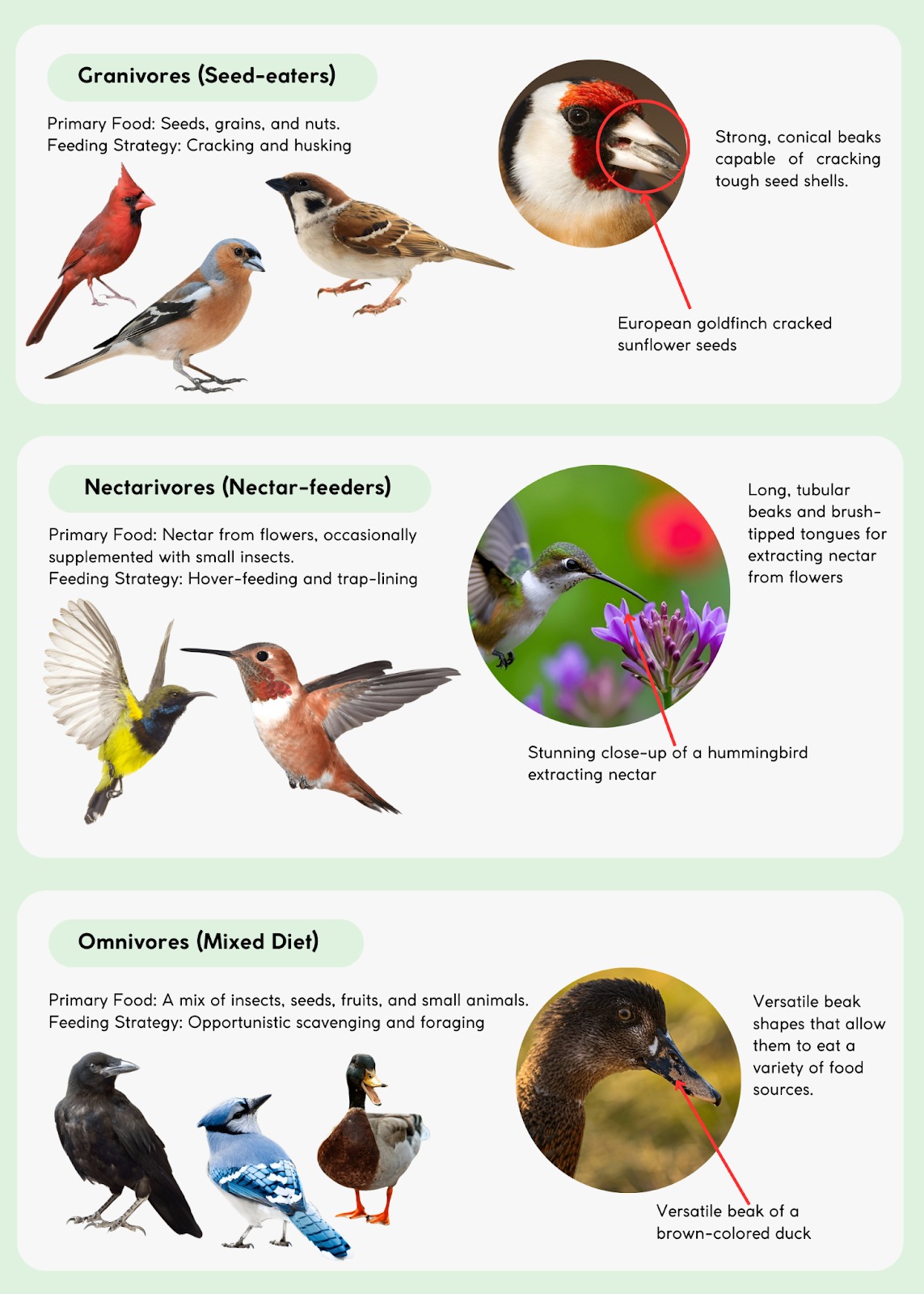
Beak Shapes And Functions
Birds have many beak shapes. The shape matches the food they eat. Beaks can be sharp, long, or strong.
Different beak types help birds catch insects, crack seeds, or eat fish.
- Sharp beaks for tearing meat
- Long beaks for reaching nectar
- Strong beaks for cracking nuts
- Flat beaks for filtering water
Wing Structure
Bird wings have bones and feathers that allow flight. The shape of wings controls how birds fly.
Some birds have broad wings for soaring. Others have narrow wings for fast flying.
- Broad wings help with gliding and soaring
- Narrow wings help with speed and agility
- Strong muscles move the wings for flight
Legs And Feet Adaptations
Bird legs and feet are adapted for walking, swimming, or perching. Different birds have different feet shapes.
Some birds have webbed feet for swimming. Others have sharp claws for catching prey.
- Webbed feet help birds swim
- Strong claws help birds hold prey
- Perching feet help birds grip branches
Flight Abilities
Birds are well known for their ability to fly. Flight helps them find food, escape danger, and migrate.
Many features work together to make flight possible. These include wing shape, muscles, and flying styles.
Types Of Flight
Birds use different types of flight depending on their needs and environment. Some fly fast, others glide slowly.
Common types of flight include flapping, gliding, soaring, and hovering. Each type helps birds in unique ways.
- Flapping:Birds move their wings up and down to gain speed.
- Gliding:Birds spread their wings and use air currents to move without flapping.
- Soaring:Birds circle in rising warm air to stay high with little effort.
- Hovering:Birds flap their wings rapidly to stay in one spot, like hummingbirds.
Wing Morphology
Wing shape affects how birds fly. Different shapes work better for speed, gliding, or maneuvering.
Birds have wings that vary in length, width, and feather arrangement to fit their flight style.
- Long and narrow wings:Good for fast, long-distance flying.
- Short and wide wings:Help with quick turns and slow flight.
- Pointed wings:Reduce air resistance for fast flight.
- Rounded wings:Provide more lift for soaring and gliding.
Flight Muscles
Strong muscles power a bird’s wings. These muscles help lift and move the wings during flight.
The main flight muscles are the pectoralis and supracoracoideus. They work together for smooth wing movement.
- Pectoralis:Lowers the wings for the downstroke.
- Supracoracoideus:Raises the wings for the upstroke.
- Both muscles are large and strong in flying birds.
Reproductive Traits
Birds have special traits that help them reproduce. These traits ensure their young can survive and grow well.
Reproductive traits include how birds lay eggs, care for their young, and find mates.
Egg Laying And Nesting
Birds lay eggs with hard shells. The shells protect the baby inside from damage and drying out.
Nesting is important. Birds build nests to keep eggs safe and warm until they hatch.
- Nests can be made from twigs, leaves, mud, or feathers
- Nests are often hidden to avoid predators
- Some birds reuse old nests, others build new ones every season
Parental Care
Most birds take care of their eggs and chicks after laying eggs. They keep them warm and safe.
Parents feed their chicks and protect them from danger until they can fly and find food alone.
- Both parents often share care duties
- Some birds feed chicks by regurgitating food
- Care time varies by species and environment
Mating Behaviors
Birds have unique ways to attract mates. They use songs, colors, and dances to show strength.
Mating often involves rituals that help birds choose the best partner for raising young.
- Male birds often sing to attract females
- Bright feathers can show health and good genes
- Some birds perform dances or build displays
Credit: animal-pedia.org
Sensory Adaptations
Birds have special senses that help them survive in nature. These senses help them find food, avoid danger, and move around.
Their sensory adaptations include sharp vision, strong hearing, and great navigation skills. Each sense works well for their needs.
Vision And Color Perception
Birds have excellent eyesight. They can see far and in many directions. Their eyes help them spot prey or danger quickly.
Many birds see colors better than humans. They can see ultraviolet light, which helps them find food and mates.
- Sharp focus helps catch small prey
- Wide field of view detects predators
- Color vision aids in finding ripe fruits and flowers
- Ultraviolet vision reveals hidden markings
Hearing Capabilities
Birds have strong hearing to listen for sounds around them. This helps them find food and hear calls from other birds.
The shape of their head and ears helps catch sounds well. Some birds can hear very high or very low sounds.
- Locate prey by sound
- Recognize calls from other birds
- Detect predators early
- Communicate with mates and chicks
Navigation Skills
Birds travel long distances during migration. They use special senses to find their way home or to new places.
Birds use the sun, stars, and Earth’s magnetic field to navigate. They also remember landmarks along their routes.
- Use the sun’s position for direction
- Navigate by stars at night
- Sense Earth’s magnetic field
- Recognize landmarks and sounds
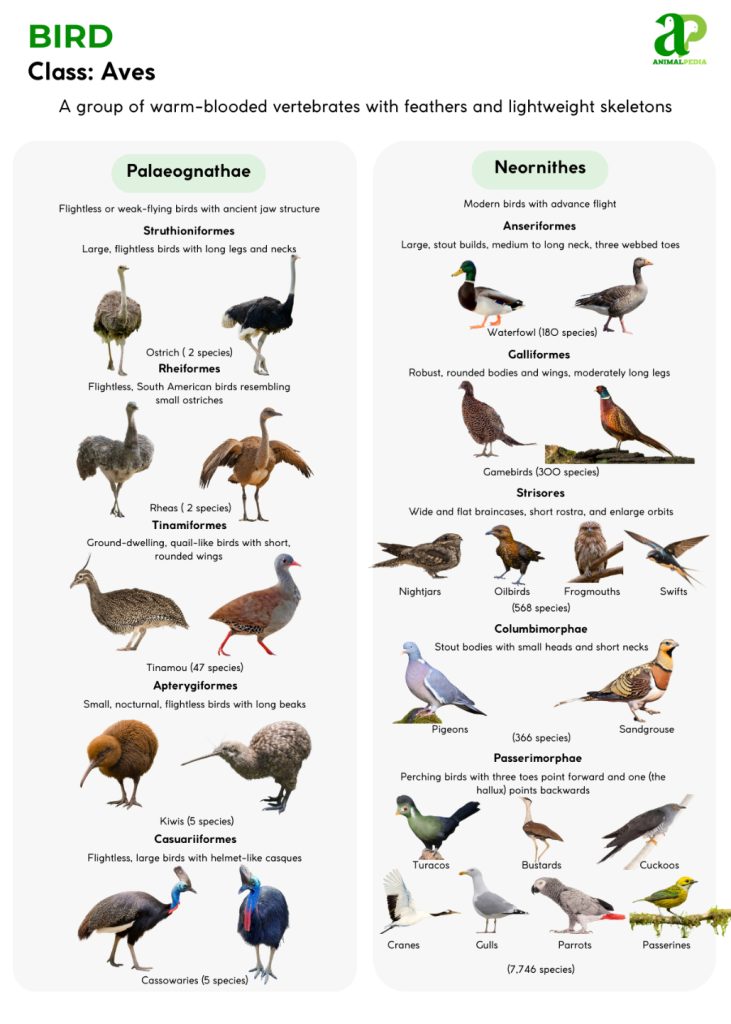
Behavioral Characteristics
Birds show many behaviors that help them survive and live in different places. These behaviors include how they move, talk, and live with others.
Understanding these behaviors helps us learn more about bird life and how they adapt to their environment.
Migration Patterns
Many birds travel long distances at certain times of the year. This travel is called migration. Birds move to find food and better weather.
Some birds fly thousands of miles to reach warm places in winter. They return to cooler areas in summer to breed and raise their young.
- Migration helps birds avoid cold weather and food shortages.
- Birds use the sun, stars, and Earth’s magnetic field to find their way.
- Not all birds migrate; some stay in one place all year.
Communication Methods
Birds use sounds and body movements to talk to each other. These communications help them find mates and warn of danger.
Bird songs are common in many species. Each bird has unique calls for different situations like attracting mates or marking territory.
- Songs and calls help birds find each other.
- Visual signals include wing flapping and feather displays.
- Some birds mimic sounds from their environment.
Social Structures
Birds often live in groups called flocks. These groups help protect them from predators and find food more easily.
Some birds form pairs or family groups to raise their young. Other species may have complex social systems with leaders and helpers.
- Flocks provide safety in numbers.
- Many birds share duties like feeding and guarding chicks.
- Social bonds strengthen survival and breeding success.
Credit: animal-pedia.org
Respiratory And Circulatory Systems
Birds have special respiratory and circulatory systems. These systems help them get oxygen and move it through their bodies. Their systems work very well to support flying and other active behaviors.
The respiratory system brings air into the body, while the circulatory system carries oxygen to cells. Both systems must be efficient for birds to stay active and healthy.
Air Sac System
Birds have a unique air sac system that helps them breathe better. Air sacs are like small balloons connected to their lungs. They store air and keep it moving in one direction.
This system allows birds to get fresh air even when they breathe out. It makes their lungs more efficient than those of mammals.
- Air sacs help move air through lungs continuously
- They allow better oxygen exchange
- Birds can breathe while flying
Efficient Circulation
Birds have a strong and fast circulatory system. Their hearts have four chambers, like humans, which keeps oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood separate.
This separation helps deliver oxygen quickly to muscles. It supports high energy needs during flight and activity.
- Four-chambered heart improves blood flow
- High heart rate pumps blood faster
- Efficient oxygen delivery to body tissues
Thermoregulation
Birds are warm-blooded animals that keep a steady body temperature. This ability helps them live in many climates.
Thermoregulation means how birds control their heat to stay healthy and active.
Body Temperature Control
Birds keep their body temperature around 40°C (104°F). They use feathers to keep warm or cool.
They fluff their feathers to trap heat in cold weather. In heat, they spread feathers to let air flow.
- Fluff feathers to trap heat
- Spread feathers to release heat
- Use blood flow to lose or keep heat
- Breathe faster to cool down
Adaptations To Climate
Birds have special features to live in different climates. These help them avoid heat loss or overheating.
For cold places, birds have thick feathers and fat to stay warm. In hot places, they have less fat and lighter feathers.
- Thick feathers and fat in cold climates
- Light feathers and less fat in hot climates
- Some birds pant to cool down
- Large bills help release heat

Credit: www.earthofbirds.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Defining Features Of Birds?
Birds have feathers, beaks, and lay hard-shelled eggs. They possess wings and a lightweight skeleton adapted for flight. Most birds also have keen eyesight and vocal communication.
How Do Feathers Benefit Birds?
Feathers provide insulation, enable flight, and aid in camouflage. They also play a role in mating displays and protecting birds from weather elements.
Why Do Birds Have Hollow Bones?
Hollow bones reduce body weight, making flight easier. This skeletal adaptation enhances agility and energy efficiency during flying.
What Role Do Beaks Play In Birds?
Beaks help birds eat, groom, build nests, and defend themselves. Their shapes vary depending on diet and habitat, reflecting adaptation to different environments.
Conclusion
Birds are unique creatures with many special traits. They have feathers, wings, and beaks. Most birds can fly, but some cannot. They lay eggs and have strong bones. Birds use their songs to communicate. These features help birds survive in nature.
Understanding these traits helps us appreciate birds more. Watching birds can be fun and relaxing. Nature’s flyers are a true wonder to see.
John James Audubon is a writer at birdopedia.com, dedicated to exploring and sharing the wonders of birds and wildlife. He writes engaging and informative articles to help readers identify, understand, and appreciate birds, combining accurate knowledge with practical tips for birdwatching and nature observation.